What is retinal detachment?
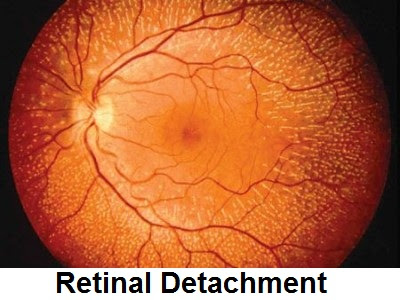
In a retinal detachment is the retina independently of the deeper layer in the eye. The portion of the retina that is released is not working properly anymore. You will notice probably because suddenly you see spots or flashing lights. In some people, is a part of the field of view clear. It may also be that you are going to see less sharp.
A retinal detachment arises because there are small cracks in the retina. If once there is a hole in the retina, moisture can get under the retina. The retina then release.
A detached retina must quickly be treated, otherwise you can be blind within a few weeks.
The ophthalmologist can treat a retinal detachment with laser or with surgery. Which treatment is best depends on how bad it is retinal detachment.
Retinal detachment can occur at any age but is more common in older people.
You have more risk of retinal detachment:
- if you have had cataract surgery;
- as retinal detachment occurs in your family;
- If you are nearsighted (you need a pair of glasses or contact lenses for distance vision).
What causes retinal detachment?
Retinal detachment caused by changes in the vitreous.
Vitreous humor is a jelly-like substance inside the eye. It sits on a number of places to the retina. In many people, the vitreous shrinks with age.
The vitreous shrinks too quickly, there may be cracks or holes in the retina occur. Is there had arisen a hole, then there can be fluid between the retina and the deeper layers of the eye. The retina then release.
Also an accident (such as a blow to the eye), retinal detachment can cause a tumor.
What are the symptoms of retinal detachment?
Everyone can see even a ' spark ' or ' substances ' in the can field. That's normal. Sudden flashes of light and dark spots that is very different than normal, can be the start of retinal detachment.
Blind spots in the can field can also point to retinal detachment. The blind spots caused by blood in the eye. That blood is released because a blood vessel is torn.
Also leaves the central part of the retina loose, then you will see blurry.
Retinal detachment diagnosis
On the outside of the eye can see nothing of a retinal detachment. Do you have symptoms such as flashing lights, dark spots, blind spots or seeing blurry? Then go to the doctor. They will refer you to an ophthalmologist if necessary.
The ophthalmologist sees with special devices or there are holes in the retina or retinal is released. To look good in your eye, you get eye drops. The eye drops make the pupil wider. By which drops you will get something less. But after a few hours, everything is back to normal.
Sometimes, an echo is necessary in order to determine whether or not it is of the retina in place. For example if the vitreous muddied by bleeding. An ultrasound scan is painless and harmless.
Ophthalmologists often have long waiting lists. You can usually go directly to an optometrist. An optometrist can see a part of the retina. If it is necessary that you get a referral to an ophthalmologist. Who does a more extensive investigation.
An optician can not determine retinal detachment.
What is the treatment for retinal detachment?
The retina can come loose through a hole in the retina. Often the ophthalmologist discovered such a hole all while the retina still stuck. Then, a laser treatment is possible. This treatment will prevent it coming off the retina.
If the retina is released all other treatments are needed. These may include:
- The ophthalmologist gas injection into the eye. This creates a bubble that seals the crack. The fluid under the retina then dissolves. Then the doctor can fix the crack. They do this with a laser or by freezing.
- The ophthalmologist places a band around the eye. This band supports the retina, and ensures that the vitreous not as hard pull on the retina. Some people are then still need additional treatment. For example, this may be a puncture. The physician then pricks in the eye to drain the fluid under the retina. Other complementary treatments are laser treatment and freezing.
- An internal eye surgery. The ophthalmologist takes away the vitreous and the retina firmly press firmly. They do this for example with a sponge silicone.
After surgery, you will probably see less sharp than before. How much less is dependent on the time between the retinal detachment and the operation.